Lab 3: Keypad Scanner
Introduction
In this lab I created code to read a keypad and display the the recent two inputs on the dual seven segment display.
Technical Documentation
The source code for this project can be found in this github repository.
Block Diagram
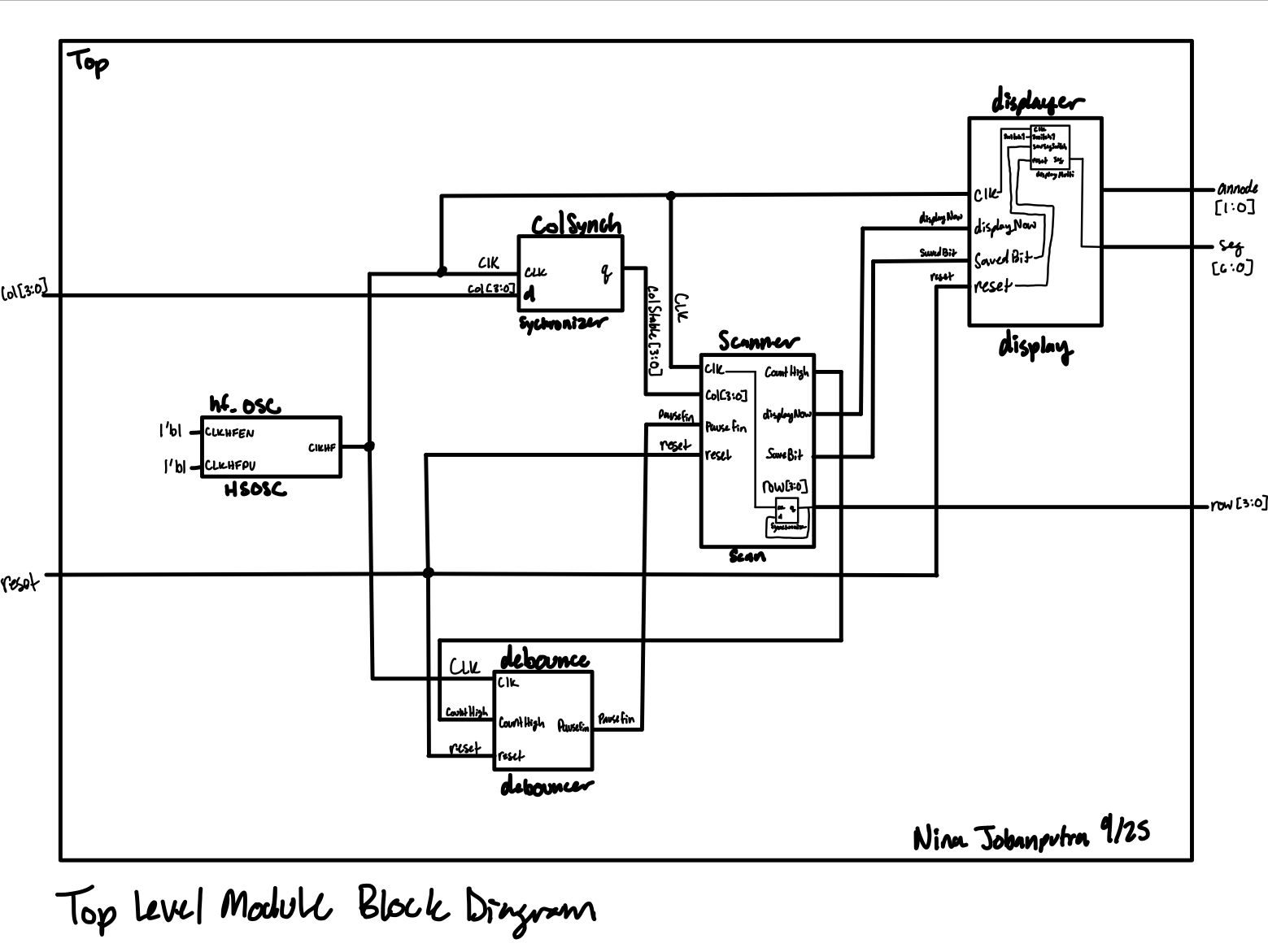
The block diagram in Figure 1 demonstrates the overall architecture of the design.
Schematic
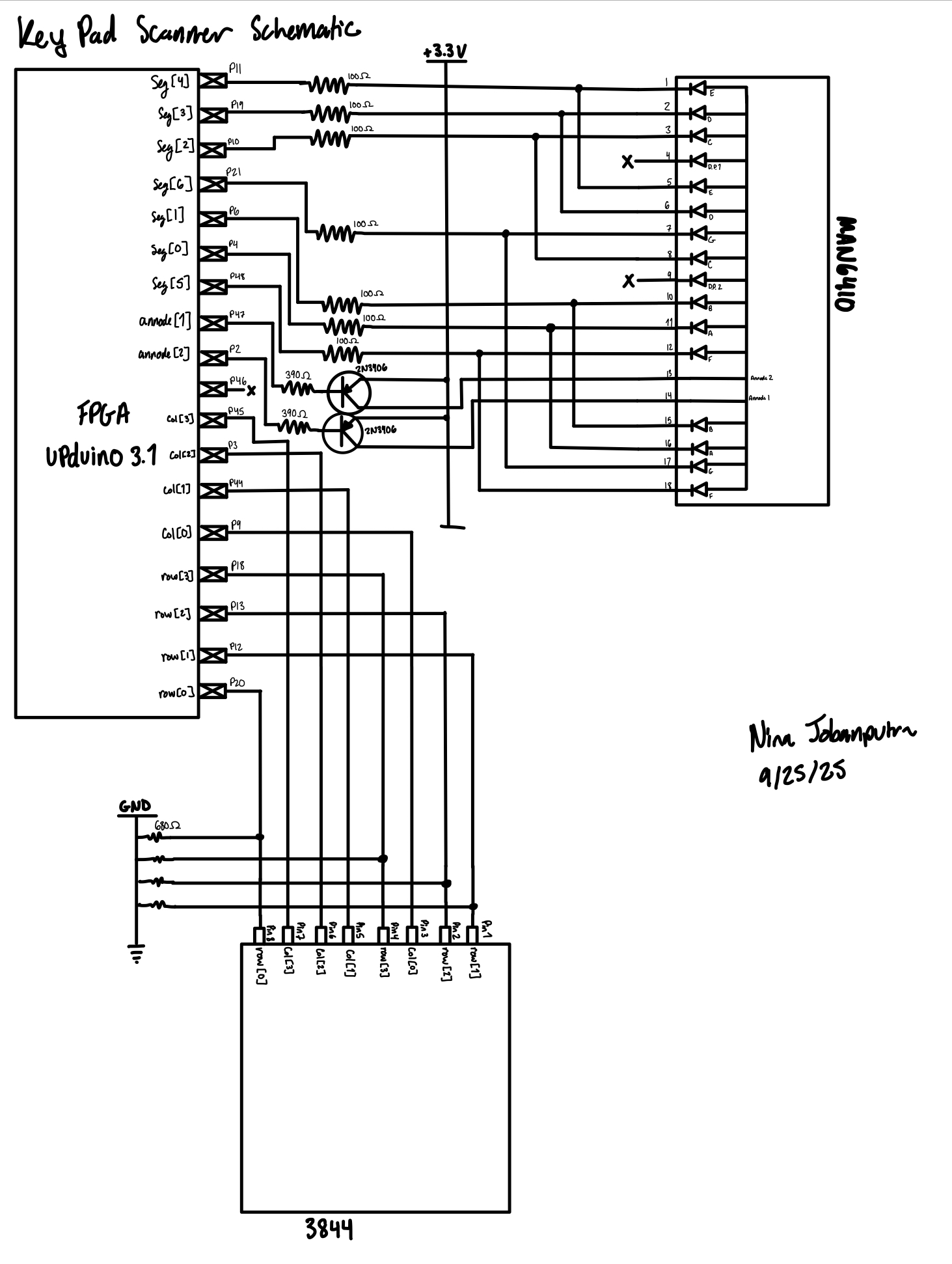
Figure 3 shows how the project was wired on my breadboard.
State Transition
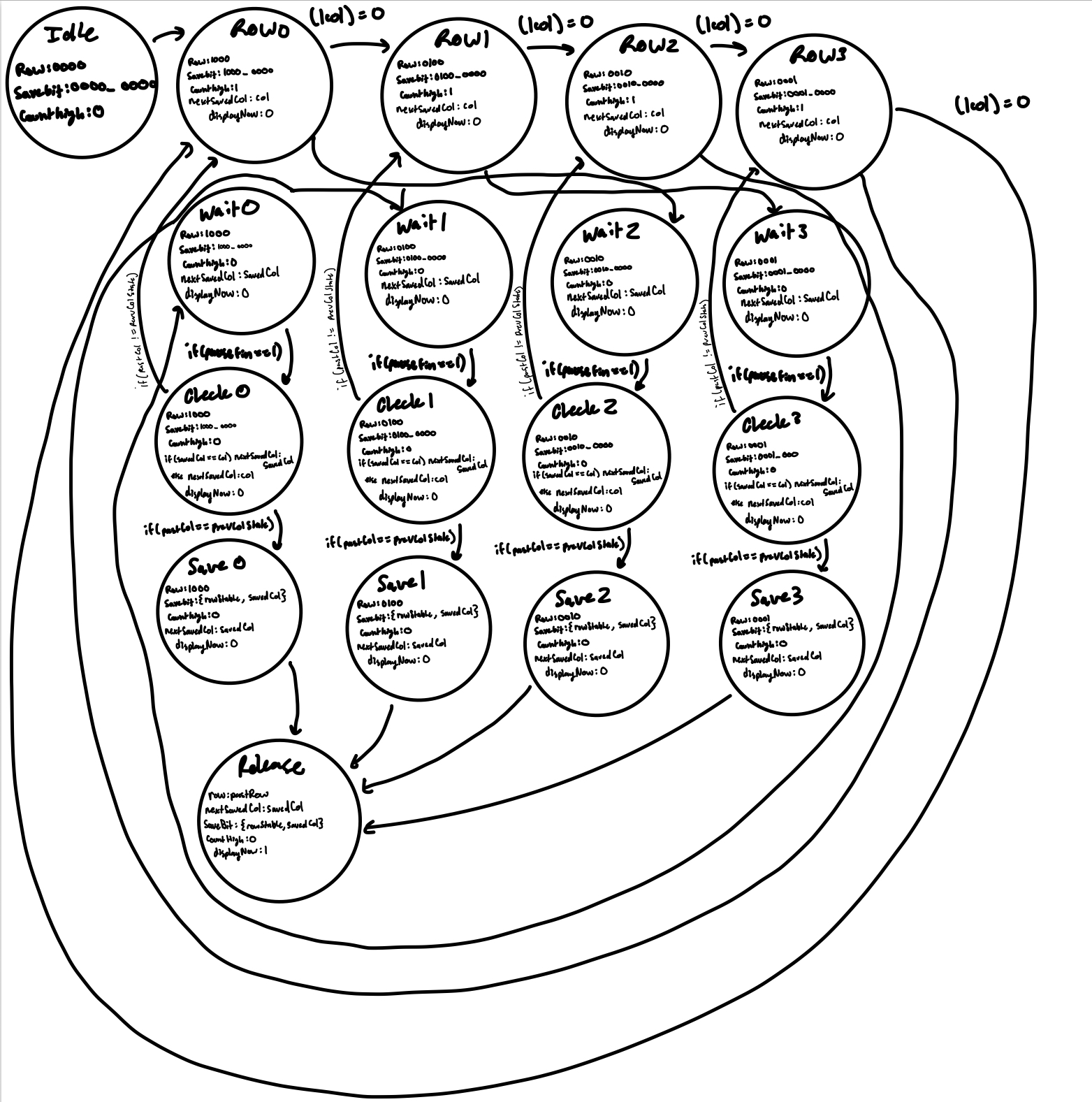
Figure 3 shows the FSM that I used in this project.
Results and Discussion
I was able to get the design working and I think I spent around 40 hours on this project. Probably would have been less if I had my brain working properly and was able to focus but I did get sick during this project so that is why it is not up to standards.
In this project I decided to power rows and take inputs of columns because this was the easiest way for me to understand. Another choice I made was using a bunch of enable signals that the entire system could talk to one another. The alternative is to include all possible states from the seperate modules together which would double the amount of states we need to use. The greater the amount of states the more output logic we have to keep track of and finding a bug in the states would have been way worse.
AI Prototype
For this AI prototype I wanted to try an AI that was not ChatGPT because in previous weeks ChatGPT hasn’t been giving the greatest code. So this weeek I used the recommended Claude. Here is the prompt I gave it: “Target device: Lattice iCE40 UP5K FPGA with internal high-speed oscillator (~20 MHz).
Write synthesizable SystemVerilog to scan a 4x4 matrix keypad and display the last two hex keys pressed on a dual 7‑segment display. Implement:
A clock divider that derives a scan clock on the order of 100–200 Hz from the internal oscillator. A keypad scanning controller that iterates one active‑low column at a time and samples active‑low rows, registering at most one key per press (debounce‑by‑design), ignoring additional presses while any key is held, and allowing a new registration only after release. A top level that updates two hex digits (older and most recent) when a new key is registered and drives a time‑multiplexed two‑digit 7‑segment display without visible flicker and with balanced brightness. Use idiomatic SystemVerilog (e.g., logic, always_ff, enumerated states for FSMs). Provide clean module boundaries and keep all state synchronous. Include brief comments explaining the design choices.”
Here is the code it gave me:
// 4x4 Matrix Keypad Scanner with Dual 7-Segment Display
// Target: Lattice iCE40 UP5K with ~20 MHz internal oscillator
// Author: Claude
// Date: 2025-09-29
//==============================================================================
// Top-level module
//==============================================================================
module keypad_display_top (
input logic clk_in, // ~20 MHz internal oscillator
input logic rst_n, // Active-low reset
// Keypad interface (active-low)
output logic [3:0] col_out, // Column drives (one low at a time)
input logic [3:0] row_in, // Row sense inputs
// 7-segment display (common cathode, assuming multiplexed)
output logic [6:0] seg, // Segments a-g (active high)
output logic [1:0] digit_sel // Digit select (active high)
);
// Internal signals
logic scan_clk; // ~100-200 Hz scanning clock
logic display_clk; // ~1 kHz display multiplexing clock
logic [3:0] key_code; // Current key pressed (0-F)
logic key_valid; // Pulse when new key registered
logic [3:0] digit0, digit1; // Two most recent keys (digit1 = newest)
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Clock dividers
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Derive ~150 Hz scan clock (20 MHz / 133333 ≈ 150 Hz)
// and ~1 kHz display refresh (20 MHz / 20000 = 1 kHz)
clock_divider #(
.SCAN_DIV(133333), // 150 Hz for keypad scanning
.DISPLAY_DIV(10000) // 2 kHz for display (1 kHz per digit)
) clk_div_inst (
.clk_in (clk_in),
.rst_n (rst_n),
.scan_clk (scan_clk),
.display_clk (display_clk)
);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Keypad scanner with debounce-by-design
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
keypad_scanner scanner_inst (
.clk (clk_in),
.rst_n (rst_n),
.scan_clk (scan_clk),
.row_in (row_in),
.col_out (col_out),
.key_code (key_code),
.key_valid (key_valid)
);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Key history register
// Shifts in new keys: digit1 gets new key, digit0 gets old digit1
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
always_ff @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
digit0 <= 4'h0;
digit1 <= 4'h0;
end else if (key_valid) begin
digit0 <= digit1; // Shift older key
digit1 <= key_code; // Store newest key
end
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Time-multiplexed 7-segment display driver
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
display_driver display_inst (
.clk (clk_in),
.rst_n (rst_n),
.display_clk (display_clk),
.digit0 (digit0),
.digit1 (digit1),
.seg (seg),
.digit_sel (digit_sel)
);
endmodule
//==============================================================================
// Clock divider module
// Generates slow clocks from the high-speed oscillator
//==============================================================================
module clock_divider #(
parameter int SCAN_DIV = 133333, // Divider for scan clock (~150 Hz)
parameter int DISPLAY_DIV = 10000 // Divider for display clock (~2 kHz)
)(
input logic clk_in,
input logic rst_n,
output logic scan_clk,
output logic display_clk
);
logic [$clog2(SCAN_DIV)-1:0] scan_counter;
logic [$clog2(DISPLAY_DIV)-1:0] display_counter;
// Scan clock generation
always_ff @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
scan_counter <= '0;
scan_clk <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (scan_counter == SCAN_DIV - 1) begin
scan_counter <= '0;
scan_clk <= 1'b1; // Single-cycle pulse
end else begin
scan_counter <= scan_counter + 1;
scan_clk <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
// Display multiplex clock generation
always_ff @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
display_counter <= '0;
display_clk <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (display_counter == DISPLAY_DIV - 1) begin
display_counter <= '0;
display_clk <= 1'b1; // Single-cycle pulse
end else begin
display_counter <= display_counter + 1;
display_clk <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
endmodule
//==============================================================================
// Keypad scanner with debounce-by-design
// Scans columns sequentially, samples rows, and registers one key per press
//==============================================================================
module keypad_scanner (
input logic clk, // System clock
input logic rst_n, // Active-low reset
input logic scan_clk, // Scan tick (~150 Hz)
input logic [3:0] row_in, // Row inputs (active-low)
output logic [3:0] col_out, // Column outputs (active-low, one at a time)
output logic [3:0] key_code, // Detected key code (0-F)
output logic key_valid // Pulse when new key registered
);
// FSM states
typedef enum logic [1:0] {
IDLE, // No key pressed, scanning
KEY_DETECTED, // Key detected, register and wait for release
WAIT_RELEASE // Waiting for all keys to be released
} state_t;
state_t state, state_next;
// Column scanning (one-hot active-low)
logic [1:0] col_index; // Which column is active (0-3)
logic [3:0] col_out_reg;
// Key detection
logic any_key_pressed; // True if any row is low (key pressed)
logic [3:0] key_code_reg;
logic key_valid_reg;
// Combinational: check if any key is currently pressed
assign any_key_pressed = (row_in != 4'b1111);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Column scanner: cycles through columns on each scan_clk
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
col_index <= 2'b00;
end else if (scan_clk && state == IDLE) begin
col_index <= col_index + 1; // Wrap around 0-3
end
end
// Generate active-low column output (one-hot)
always_comb begin
col_out_reg = 4'b1111; // All high (inactive)
col_out_reg[col_index] = 1'b0; // Drive selected column low
end
assign col_out = col_out_reg;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Key code calculation from row and column
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
function automatic logic [3:0] calc_key_code(logic [1:0] col, logic [3:0] row);
logic [3:0] code;
// Standard 4x4 keypad layout (hex):
// Row 0: 1 2 3 A
// Row 1: 4 5 6 B
// Row 2: 7 8 9 C
// Row 3: * 0 # D (mapping * to E, # to F)
case ({col, row})
// Column 0
6'b00_1110: code = 4'h1; // Row 0, Col 0
6'b00_1101: code = 4'h4; // Row 1, Col 0
6'b00_1011: code = 4'h7; // Row 2, Col 0
6'b00_0111: code = 4'hE; // Row 3, Col 0 (*)
// Column 1
6'b01_1110: code = 4'h2; // Row 0, Col 1
6'b01_1101: code = 4'h5; // Row 1, Col 1
6'b01_1011: code = 4'h8; // Row 2, Col 1
6'b01_0111: code = 4'h0; // Row 3, Col 1
// Column 2
6'b10_1110: code = 4'h3; // Row 0, Col 2
6'b10_1101: code = 4'h6; // Row 1, Col 2
6'b10_1011: code = 4'h9; // Row 2, Col 2
6'b10_0111: code = 4'hF; // Row 3, Col 2 (#)
// Column 3
6'b11_1110: code = 4'hA; // Row 0, Col 3
6'b11_1101: code = 4'hB; // Row 1, Col 3
6'b11_1011: code = 4'hC; // Row 2, Col 3
6'b11_0111: code = 4'hD; // Row 3, Col 3
default: code = 4'h0; // No valid key
endcase
return code;
endfunction
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// FSM: debounce-by-design state machine
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
end else begin
state <= state_next;
end
end
always_comb begin
state_next = state;
case (state)
IDLE: begin
// Scanning columns, looking for a key press
if (scan_clk && any_key_pressed) begin
state_next = KEY_DETECTED;
end
end
KEY_DETECTED: begin
// Key registered, now wait for release
state_next = WAIT_RELEASE;
end
WAIT_RELEASE: begin
// Wait until all keys released before accepting new press
if (scan_clk && !any_key_pressed) begin
state_next = IDLE;
end
end
default: state_next = IDLE;
endcase
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Output registration
// Generate key_valid pulse and latch key_code when transitioning to KEY_DETECTED
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
key_code_reg <= 4'h0;
key_valid_reg <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (state == IDLE && state_next == KEY_DETECTED) begin
// Capture key code at the moment of detection
key_code_reg <= calc_key_code(col_index, row_in);
key_valid_reg <= 1'b1; // Pulse for one cycle
end else begin
key_valid_reg <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
assign key_code = key_code_reg;
assign key_valid = key_valid_reg;
endmodule
//==============================================================================
// 7-segment display driver with time multiplexing
// Alternates between two digits at ~1 kHz rate for flicker-free display
//==============================================================================
module display_driver (
input logic clk,
input logic rst_n,
input logic display_clk, // Multiplex clock (~2 kHz)
input logic [3:0] digit0, // Older digit (left)
input logic [3:0] digit1, // Newer digit (right)
output logic [6:0] seg, // 7-segment outputs a-g
output logic [1:0] digit_sel // Digit selection (one-hot)
);
logic current_digit; // Which digit to display (0 or 1)
logic [3:0] hex_value;
// Alternate between digits on each display_clk tick
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
current_digit <= 1'b0;
end else if (display_clk) begin
current_digit <= ~current_digit;
end
end
// Select which hex value to display
assign hex_value = current_digit ? digit1 : digit0;
// Generate digit select signals (one-hot active high)
assign digit_sel = current_digit ? 2'b10 : 2'b01;
// Hex to 7-segment decoder
// Segments: {g, f, e, d, c, b, a} - active high
always_comb begin
case (hex_value)
4'h0: seg = 7'b0111111; // 0
4'h1: seg = 7'b0000110; // 1
4'h2: seg = 7'b1011011; // 2
4'h3: seg = 7'b1001111; // 3
4'h4: seg = 7'b1100110; // 4
4'h5: seg = 7'b1101101; // 5
4'h6: seg = 7'b1111101; // 6
4'h7: seg = 7'b0000111; // 7
4'h8: seg = 7'b1111111; // 8
4'h9: seg = 7'b1101111; // 9
4'hA: seg = 7'b1110111; // A
4'hB: seg = 7'b1111100; // b
4'hC: seg = 7'b0111001; // C
4'hD: seg = 7'b1011110; // d
4'hE: seg = 7'b1111001; // E
4'hF: seg = 7'b1110001; // F
default: seg = 7'b0000000; // Blank
endcase
end
endmoduleOne thing I found interesting between it and my code is that it only used 3 states in their FSM. This is what I had originally planned on but couldn’t get it to work. When I did try to run the code I got some errors that made it unable to synthesize but overall it seems similar to the code I have written. I woner if it could be used to bebug my code well since I found forums weren’t as helpful when I was debugging.